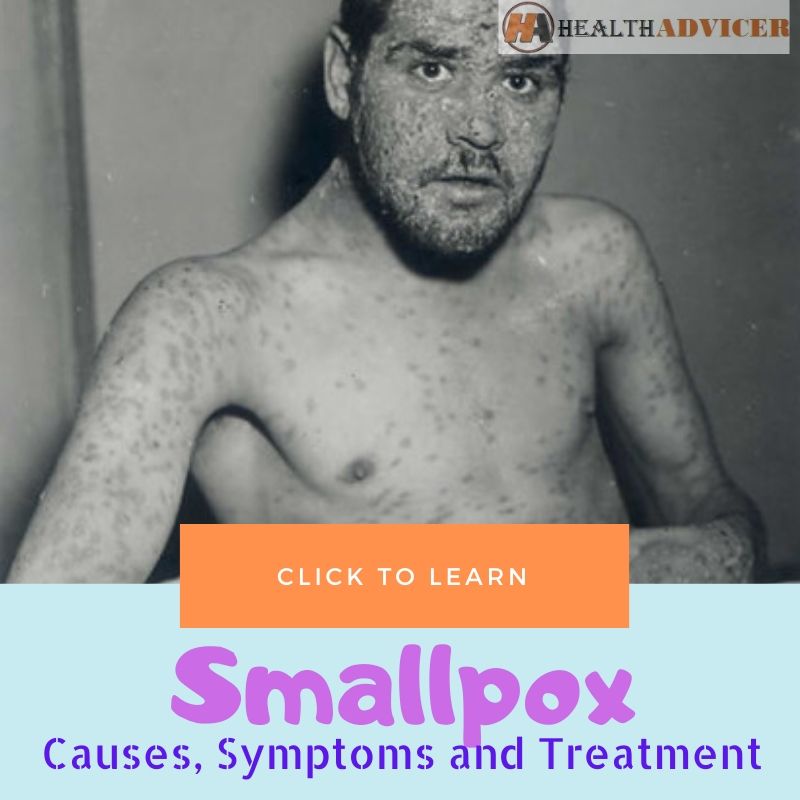
Smallpox is a contagious disease with deadly results. It has affected people for more than a thousand years. The disease disfigures people and often leads to death. Thanks to the research and successful eradication campaign, eradication of the naturally occurring disease has become possible. The WHO (World Health Organization) has declared it eradicated by the year 1980. It is the result of unprecedented immunization campaigns across the globe. But, samples of the virus are still saved for research purposes. So, it has led to the concern of using it as an agent for global biological warfare.
Since no cure is present for the disease, it has led to immense concerns among people. You have no effective treatment or cure available for the disease. Getting a vaccination can prevent the disease. But, it is not advised in general cases due to the severity of side effects associated with it. Read ahead to know more about the deadly disease.
History Of Smallpox
You may have read stories about the deadly results of smallpox. Do you know that the disease has existed for more than 12,000 years? Evidence suggests even ancient mummies from Egypt suffered by infection due to the virus. The origin of the disease in the world dates back to the 16th century. European explorers and conquerors (conquistadors). Since the native aboriginal inhabitants never developed immunity to such diseases, the deadly virus resulted in the death of the native population. Unfortunately, it resulted in the first-ever biological warfare as people intentionally infected variola virus on the Native American population using contaminated blankets in the 18th century. Reports suggest that smallpox caused the death of 300 million to 500 million people around the world in the 20th century. It is high compared to other diseases like tuberculosis (100 million deaths).
At the end of the 18th century, English scientist Edward Jenner discovered an effective method of vaccination. His research discovered milkmaids having immunity to the deadly disease. Milkmaids developed the immunity to variola major virus as they developed mild cowpox. The antibodies of cowpox offered immunity to the deadly disease. His strategy involved transferring the cowpox blister fluid from an infected person to a normal person. The process, also known as variolation cause the person to develop mild cowpox infection. But, it offered protection against variola virus. Scientists have developed vaccinia that mimics the effect of the cowpox virus. You have no reason to fear for the disease as WHO has eradicated it. It is the first disease to get eliminated from the world. Now campaigns are underway to eradicate other diseases like measles and polio.
Symptoms Of Smallpox
The deadly disease can trigger several symptoms within ten or fourteen days of the infection. So, you can see the first symptoms within two weeks of the exposure to variola virus. After the exposure, you may feel healthy as the incubation period of seven to seventeen days does not cause any signs. So, you look and feel healthy. The virus is also not contagious during the period. After the incubation period, you develop flu-like signs. So, you can see symptoms like:
- Headache
- Overall discomfort
- Fever
- Severe back pain
- Severe fatigue
- Possible Vomiting
You can develop a rash on the following areas of your body:
- Hands
- Face
- Forearms
- Trunk
After one or two days, the sores developed can turn into blisters filled with a clear liquid. It can then turn into pus. You can also develop lesions on your mucous membranes on areas like nose and mouth. These sores can break open. After eight or nine days, the scabs can form and fall off. It results in deep, pitted scars.
Stages Of Smallpox
How does a person develop the disease? It can develop in different stages. The risk of spread also differs with each stage. The different stages are:
Incubation Period
It is the period when the virus enters your body and starts attacking your immune system. The incubation period refers to the length of time taken to see visible signs of sickness. It can range from seven to nineteen days. Most people may see little or no signs. It is also not contagious. So, you may feel fine.
Initial Stage
The stage tends to last from two to four days. The virus can sometimes become contagious. But, the next two phases poses more risk of spreading it to others compared to the initial stage. During the stage, you can develop the following signs:
- Head and body aches
- High fever
- Nausea or vomiting (sometimes)
At this time, people are usually too sick to carry on their normal activities.
Early Rash
It is the most contagious phase of the disease. It can last for about four days. During the stage, you can see a rash developing. It appears as small red spots, which can turn into sores. They tend to appear in your mouth and tongue. The sores can break open in the mouth and tongue. So, it spreads a large amount of variola virus into the throat and mouth. The affected person continues to suffer from a fever.
As the sores in the mouth and tongue start to breaks down, the affected person can see rashes appearing on other parts of the body. It first appears on the face and spreads to arms as well as legs. The rash can also develop on hands and feet. People can see rash appearing on different parts of the body within twenty-four hours. After the appearance of the rash, fever tends to decline. So, the affected person feels better. But, by the fourth day, the sores fills with opaque, thick liquid with a dent in the middle. You refer to the sores with fluid as pustules. The fever rises again and remains the same until you develop scabs form over the sores.
Pustular Rash And Scabs
You develop pustules, which has a round and sharply raised appearance. It feels a little firm to touch. So, you feel like touching peas under your skin. The pustular rash tends to form a crust after five days and then scab. The virus is contagious during the stage. The phase can last for two weeks and by the end of the second week, all the sores developed on the patient’s body scabs over.
Scabs Fall Off
Three weeks after you develop the rash, the scabs tend to fall off. During this time, it is contagious as the virus has more chances to spread. The falling off scabs can leave permanent marks on the skin.
Scabs Fade
After the scabs fall off, the virus becomes noncontagious. It occurs four weeks after you develop the rash. Once all scabs fall off, the patient can resume their normal life.
Causes Of Smallpox
You suffer from the disease due to the infection by the variola virus. When the virus affects your immune system, you can become affected by the problem. In normal cases, the virus transmits in the following methods:
Direct Contact
The virus spreads from one infected person to a healthy person when they come in contact. For direct transmission of the virus, you need prolonged contact face-to-face. So, spending some time with an infected person can increase your chances of getting the virus through air. It occurs when the droplets with the virus reach the normal person when the infected person talks, sneezes or coughs.
Indirect Contact
While it is rare, indirect contact with an infected person can also spread the virus. The airborne variola virus can spread from the infected person through the ventilation system in the building. So, it infects the people staying on other floors or rooms.
Contact With Contaminated Items
You can get infected by the virus by coming in contact with contaminated items. When you touch the items used by an infected person, the chances of variola virus spreading increases. So, you can get the infected by touching the contaminated clothing, bedding or other personal items. But, unlike direct contact, the risk of infection from the above-mentioned sources are less common.
Bio-Weapon
Since the eradication of the virus and disease, the chance of getting it today through other ways are less. You can suffer from the problem when used as a biological weapon by terrorists. As several research facilities across the world have a sample of the smallpox virus, a deliberate release can pose a huge threat. But, government officials have taken numerous steps to tackle such issues. So, as soon as the release of the virus occurs, the officials take action to prevent the spreading of disease with effective steps. These precautions can protect people against the possibility of getting infected. The steps include stockpiling vaccination to prevent the virus from affecting.
Risk Factors Of Smallpox
In the past, the infection occurred due to coming in contact with smallpox infected person. Close association with another person with the disease increases the risk of getting the infection. So, when you come in contact with the virus-contaminated drops from the infected person, your chance of getting smallpox increases. The droplets come from the sneezes and coughs. While it is infrequent, you can also develop infected by touching heavily contaminated items used by the virus-infected person. It can transfer the virus to your mucous membranes. So, caretakers of the virus-infected person can face the risk of developing the disease.
Currently, people working in highly specialized laboratories dealing with the virus face the risk. The viruses in the storage box pose a high risk of contamination. So, when a lab tech, transporter or vaccinator comes in contact with it accidentally while working with the viruses or who deliberately use it as a biological weapon can face the threat of developing the disease.
Transmission And Contagious Nature Of Smallpox Virus
The majority of people get the virus from direct transmission from an infected person. When you come in contact with large droplets of saliva expelled during sneezing or coughing of infected people, it can cause the transmission of the virus. The transmission occurs similarly to influenza, measles or mumps. So, it requires close face-to-face contact with the infected person. Indirect transmission can also cause the spread of the disease. An infected person can cause a 60% contamination of the household items. The heavily contaminated bedding or silverware can carry a sufficient number of viruses to infect a healthy person. In most cases, improper handling of personal items leads to the transmission of the virus.
Smallpox is a highly contagious disease, which remains contagious until the scabs on the patient fall off. It takes around three to four weeks for the contagious period to end. It is calculated from the initial rash development. The incubation period of the virus slights differs from the others. It is a little longer compared to other viruses. Once a person gets exposed to the virus, it takes seven to seventeen days to develop the symptoms.
Complications Associated With Smallpox
The virus can cause devastating effects on people it affects. While most people affected by the virus can survive, they can experience several issues like:
Disfigurement
People who recover from smallpox have severe scars on the affected places. It is more prominent in the visible areas of the body like face, legs, and arms. It affects the visual appeal of affected people. So, they tend to avoid social interaction due to the unsavory looks and comments.
Blindness
In some cases, the virus affects the eyes. So, it can lead to blindness.
Death
A few rare varieties of the variola virus can cause fatal results. The severe forms of the virus mostly affected people with a weakened immune system. So, people suffering from some underlying health problems causing a weak immune system or pregnant women face the risk of severe effects of the virus. It can lead to death.
Diagnosis Of Smallpox
Since it is an eradicated disease, doctors can find it difficult to diagnose the issue today. So, if a smallpox outbreak occurs, the doctors cannot diagnose the problem in its initial stages. They may not realize the problem, which increases the possibility of spreading the disease. A definitive test is available with the CDCP (Center for Disease Control and Prevention). The following methods can detect the presence of variola virus:
Check Lesion
The technicians extract the sample tissue from the skin lesion of the infected person. The technicians test it in the lab for conclusive evidence. Isolation of the virus present in the lesion can confirm the diagnosis.
Antibodies Presence
The blood sample from the infected person can show the presence of antibodies made by the immune system in response to the virus. It can help detect the problem without any room for doubts.
The diagnosis for the condition always occurs in a specialized laboratory with the latest testing techniques. The lab also has to take measures to protect the technicians from exposure to the virus. The governments around the world consider the disease as an international health emergency. So, the associated agencies deal with even a single confirmed case with care and caution. The lab takes adequate steps to isolate the patient and prevent its spread. The disease remains contained and does not cause further complications due to the utmost care taken by the technicians.
Treatment For Smallpox
You need to understand that no cure is available for smallpox. The treatment is supportive in nature. So, necessary steps aim to reduce the severity of the symptoms. The doctor can suggest the following steps:
Isolation
Patients suffering from the condition need hospitalization. In hospitals, the doctors and healthcare staff follow strict airborne and contact isolation procedures. It includes checking the rooms for HEPA air filters and negative air pressure. It helps avoid spreading the virus to others.
Hydration
Patients suffering from the condition need to stay hydrated. So, it is essential to drink water or other fluids throughout the day.
Manage Fever
A patient affected by variola virus can suffer from fever. So, they need to take acetaminophen or similar medication to relieve the discomfort.
Blood Pressure Support
People infected by the virus can experience a change in blood pressure. So they need close monitoring to ensure the fluctuation does not cause an adverse effect on their health.
Deal With Accidental Contamination
Technicians work in the lab can come in contact with the variola virus accidentally. VGIV (Intravenous Vaccinia Immunoglobulin) is used in case of accidental contamination of mouth or eyes.
Preventing Smallpox
The World Health Organization (WHO) commemorated the fortieth anniversary of eradicating the deadly disease from the world. On 9th December 1979, WHO officially announced the good news. After five months, the World Health Assembly also declared the eradication of the disease. So, in May 1980, the world officially won its freedom from the deadly disease. So, it avoids the fear of getting the disease. But, what steps do you need to take in case of an unexpected outbreak? Never worry as the following steps can help prevent the problem from becoming fatal.
Isolation
In the event of an outbreak, the government agencies try to isolate the infected people in an effort to contain the disease. It avoids the spread of deadly diseases. Caretakers or anyone coming in contact with the infected people need to take vaccination to prevent or reduce the severity associated with the disease. It is essential to take the vaccination within four days of viral exposure to limit its complications.
Get Vaccination
Vaccination is the only effective method to prevent the deadly disease. Now you may wonder why it is not included in the general vaccination program. The vaccine uses a live virus to restrict the attack of variola virus on the immune system. But, the virus can cause serious complications in some rare cases. So, people can suffer from issues to the brain or heart. Since the risks outweigh the benefits, the vaccine is not recommended for everyone. It is only advised when the outbreak of the disease occurs. Depending on the time you get vaccination after your exposure, the results vary. So, you can expect the following:
- When you get the vaccine before coming in contact with an infected person or the virus, it protects you from getting sick.
- Taking the vaccine three days after exposure to the virus can protect you from getting infected by the virus. Some people can still suffer from the infection. But, the vaccine can reduce the effects on the body compared to not getting the vaccination.
- If you get the vaccine four to seven days after getting exposed to the virus, it protects you from the disease to a certain extent. While you have high chances of getting the disease, it may not cause severe symptoms as the unvaccinated person suffers.
Use Of Antiviral Drugs
Lab tests show the effectiveness of using antiviral drugs to combat the virus causing the deadly disease. But, the tests are not performed on actual people who are sick from the disease. But, in case of an outbreak, it acts as an ideal preventive and treatment option to deal with the condition.
About Vaccination And Revaccination For Small Pox
The vaccination to prevent smallpox is not available currently to the general public. It is because the WHO has eradicated the disease from the world. So, the virus is no longer present in nature. But, several countries have stocks of vaccination to prevent any issues to its citizens in the event of an outbreak.
People who have obtained vaccination as a child may wonder how long the immunity lasts. Full or partial immunity to the disease after the vaccination can last from ten years and twenty when you get revaccinated. When an outbreak occurs, it is important to receive new vaccination after coming in direct contact with people carrying the virus.
Conclusion
Smallpox is a deadly disease with irreversible complications. It has killed more people over several centuries compared to all other infectious diseases combined. The effective immunization campaign by WHO has put a stop to the disease. Its spread has now stopped and continues to remain the same after three decades. But, the possibility of bioterrorists using the samples available in the lab to attack people still remains. Several countries around the world have the necessary resources to deal with such a scenario and avoid any complications to the people. Therefore, you can remain safe and enjoy peace of mind.
View Article Sources